UPNEEQ eye drops for ptosis
What is Upneeq?
Upneeq is a prescription medication used to treat acquired blepharoptosis. A topical ophthalmic solution (oxymetazoline hydrochloride 0.1%), Upneeq is the first medication approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to temporarily improve acquired ptosis.
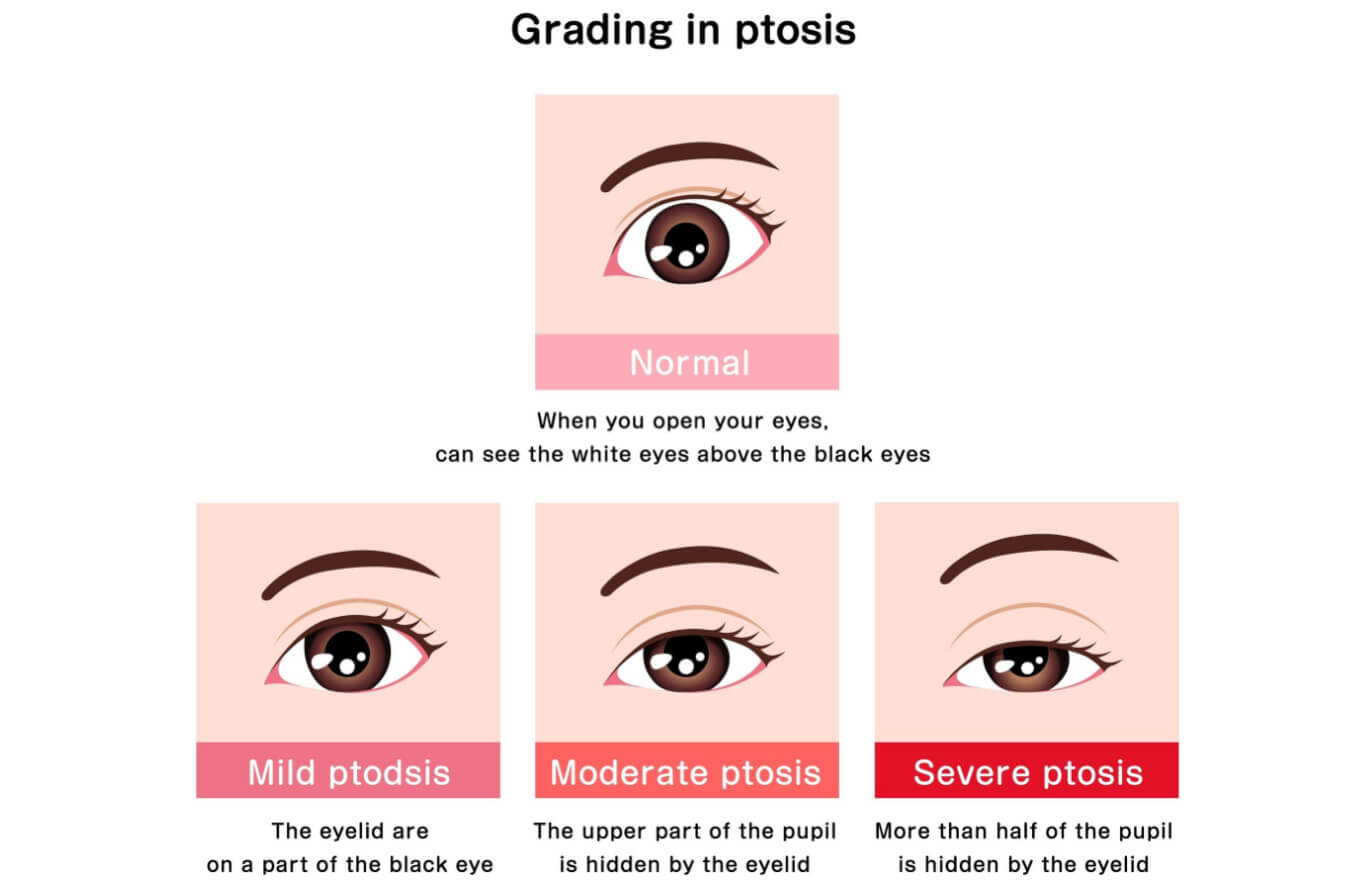
This eyelid condition can affect one or both of the eyes and is characterized by low-lying or droopy upper eyelids. Blepharoptosis is also referred to simply as ptosis (“TOE-sis”).
Upneeq is used to treat the condition of droopy eyelids in adults. When administered properly, it can help maintain the raised position of the upper eyelid. It can also contribute to visual field improvement. The results can cause the eye to be more open and look more alert.
It is estimated that approximately 11.5% of adults have ptosis. Low-lying eyelids can have an aesthetic effect on a person’s appearance, making the eyes look hooded and appear tired.
Drooping eyelids can also impair a person’s visual field if the eyelid falls over the pupil of the eye. This may impact their ability to drive, read, use a computer or look upward with an unobstructed view.
Eye conditions treated by Upneeq
Ptosis is a common upper eyelid condition. It can be acquired or congenital (present at birth).
Eyelid elevation is controlled by the levator palpebrae superioris (LPS) muscle and the superior tarsal muscle (or Muller's muscle). The levator palpebrae superioris lifts the upper eyelid and keeps it raised.
Muller’s muscle is an involuntary muscle that assists the LPS muscle in maintaining the eyelid in a raised position. When the muscles or the nerves supplying them are damaged, they fail to function properly. The eyelid begins to droop, resulting in ptosis.
Upneeq acts on Muller’s muscle by stimulating it to contract, helping to maintain the elevated eyelid. Upneeq may be used to treat the following forms of ptosis:
Acquired blepharoptosis
Acquired blepharoptosis can occur at any point in life. It is commonly caused by age or injury. In some cases, ptosis may result following eye treatment or surgical procedure.
Acquired ptosis can also be caused by:
Contact lens wear and insertion.
Surgical instruments used to keep the eye open during eye surgery.
Other health conditions.
Acquired ptosis may also signal the presence of a serious medical concern. When it occurs in only one eye, ptosis can cause the eyes to appear asymmetrical.
Age-related ptosis
Age is often a reason for droopy eyelids in adults. As people get older, the muscles supporting the upper eyelid can become stretched or weakened. The eyelid skin begins to stretch and sag as well. This may cause the eyelid to sit lower on the eye.
BOTOX-induced ptosis
Ptosis is a common side effect of BOTOX injections in the brow area. In these cases, Upneeq may be used to improve this effect and treat acquired ptosis due to BOTOX injections.
Upneeq before and after
The results of Upneeq can vary among individuals. In clinical trials, participants experienced an average of 1mm lift in the upper eyelid with the first use of Upneeq.
How does it work?
Upneeq contains a drug that acts directly on Muller’s muscle. Once administered, the solution causes Muller’s muscle to contract. This contraction lifts the eyelid to expose more of the eye.
Upneeq eye drops are manufactured in single-use containers packaged in a foil pouch. Each vial contains enough dosage to treat both eyes. Upneeq is self-administered by patients and should be used once per day.
One drop should be placed in one or both eyes. Patients who wear contact lenses should remove the lenses before inserting Upneeq eye drops. Contact lenses can be reinserted 15 minutes following the use of Upneeq.
Patients who also use other types of eye drops should wait 15 minutes between applying Upneeq and other medications.
Patients should only use Upneeq as directed.
How long does it last?
Upneeq must be administered once per day to maintain its effects. In clinical studies, some individuals experienced results within five minutes of receiving Upneeq. Most experienced results within two hours of administering the medication. The effects of a single dosage lasted as long as six hours in a number of participants.
Upneeq eye drops can be used long-term.
Who is a candidate?
Ideal candidates for Upneeq drops may include adults who have mild to moderate acquired ptosis. Those with age-related droopy eyelids and BOTOX- or speculum-induced ptosis may also be candidates for this treatment option.
Upneed is not designed for patients who have congenital ptosis and has not been tested in children. It is also not intended to treat ptosis due to trauma, nerve issues, eyebrow sagging, or eyelids that droop due to excess skin.
Risks and side effects of Upneeq
Upneeq was determined to be safe and well-tolerated when used once daily during clinical trials. These studies took place over the course of 14 to 84 days.
During Upneeq clinical trials, common side effects were observed in 1%-5% of participants. These included:
Eye irritation
Eye redness
Headache
Eye pain (upon instillation)
Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should consult their physician before using Upneeq drops. Individuals with the following conditions should also check with their doctor before using this ophthalmic solution:
High blood pressure
Low blood pressure
Heart conditions
Cerebral insufficiency
Coronary artery disease
Patients should also seek medical care if any of their conditions worsen or they develop any of the symptoms outlined above.
Drug interactions may occur with certain medications. These include blood pressure medications, heart medications, monoamine oxidase inhibitors and alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonists. Patients should consult their physician for more information on potential risks, side effects, drug interactions and adverse reactions.
Upneeq vs. surgery
Until recently, the main options for treating droopy eyelids were ptosis surgery and the use of off-label drugs, which could not be used long-term.
The surgical procedure may involve a minor adjustment to the eyelid muscles in some cases. In others, the muscle may need to be strengthened or reattached to allow for eyelid lifting. Surgery carries additional risks and potential side effects, in addition to a recovery period. Surgery is rarely recommended for cases of mild ptosis.
Upneeq offers a safe and potentially long-term nonsurgical alternative to treating acquired ptosis. Individuals may opt for Upneeq over blepharoplasty (eyelid surgery) if they are not candidates or are not yet ready for a surgical procedure.
Upneeq vs. BOTOX
BOTOX has also served as a nonsurgical option for treating mild cases of droopy eyelids by lifting the eyebrows slightly. It is commonly used to lift the eyebrows and treat fine lines and wrinkles on the upper face.
Sometimes, the use of BOTOX for lifting the eyebrow causes drooping of the eyelids because the drug has affected the nerve that controls eyelid muscles. In these cases, Upneeq may be recommended to provide a nonsurgical eyelid lift.
How much does Upneeq cost?
The cost of Upneeq may vary per location and pharmacy. On average, Upneeq costs around $228.00 for a 30-day supply.
READ NEXT: Types of ptosis
First prescription fix for drooping eyelid. American Academy of Ophthalmology. September 2020.
Ptosis (Blepharoptosis) in adults. Medscape. July 2020.
Label: UPNEEQ-oxymetazoline hydrochloride ophthalmic solution/drops. DailyMed. National Library of Medicine. May 2023.
UPNEEQ (oxymetazoline hydrochloride ophthalmic solution), 0.1%. Accessed May 2023.
Ptosis. American Optometric Association. Accessed May 2023.
Safety of once-daily oxymetazoline HCl ophthalmic solution, 0.1% in patients with acquired blepharoptosis: results from four randomized, double-masked clinical trials. Clinical Ophthalmology. November 2022.
Ptosis, congenital. EyeWiki. American Academy of Ophthalmology. January 2023.
Anatomy, Head and Neck: Eye Superior Tarsal Muscle (Muller Muscle). StatPearls. September 2022.
What is ptosis? American Academy of Ophthalmology. September 2022.
Taking a closer look at acquired blepharoptosis. Optometry Times. November 2021.
Ptosis (drooping eyelid). Cleveland Clinic. March 2019.
Botulinum toxin–induced blepharoptosis: anatomy, etiology, prevention, and therapeutic options. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. August 2021.
Upneeq FDA approval history. Drugs.com. September 2020.
NDA 212520. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. July 2020.
FDA approves Upneeq. Drugs.com. July 2020.
Use of botulinum toxin for the correction of mild ptosis. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology. April 2018.
Techniques of eyebrow lifting: a narrative review. Journal of Ophthalmic and Vision Research. April 2020.
How does botulinum toxin (Botox) work? American Academy of Ophthalmology. March 2021.
Upneeq prices, coupons and patient assistance programs. Drugs.com. Accessed May 2023.
Page published on Wednesday, May 17, 2023
Page updated on Tuesday, May 23, 2023
Medically reviewed on Monday, April 24, 2023






