Eye strain

What is eye strain?
Eye strain is a group of symptoms that happens when your eyes are overworked from a long period of focus. You can get eye strain if you have normal 20/20 vision, but uncorrected eye problems could put you at a higher risk.
The medical term for eye strain is asthenopia.
What is digital eye strain?
Digital eye strain is a type of eye strain specifically caused by looking at digital screens. "Regular" eye strain can result from other activities too, like driving or reading a book.
Another name for digital eye strain is computer vision syndrome.
Eye strain symptoms
Different people can feel the effects of eye strain in different ways. You may have one or more of these common symptoms:
Achy or tired eyes
Red, stinging or itchy eyes
Watery eyes
Difficulty focusing
Difficulty keeping your eyes open
Headaches
Pain in your neck, back or shoulders
While eye strain symptoms are uncomfortable, they don't permanently damage your eyes or vision. However, some unrelated eye conditions can cause symptoms that resemble eye strain. Schedule an eye exam if your symptoms are severe or don't go away.
Causes of eye strain
You can get eye fatigue from almost any activity that involves intensely focusing your vision for a while.
Digital screens are a well-known cause of eye strain, found on devices such as:
Computer monitors
Laptops
Cell phones
Tablets
TVs
E-readers
Handheld gaming consoles
Screens aren't the only things that can lead to visual fatigue. Some other possible eye strain causes include:
Reading a book, magazine or other printed material
Writing
Driving long distances
Sewing or knitting
Painting or sketching
Playing board games or working on puzzles
Why do screens cause eye strain?
There are a few main reasons why digital screens are particularly tiring for your eyes:

To ease eye strain, make sure you use good lighting and sit at a proper distance from the computer screen.
They're hard work – Your eyes need to constantly focus and refocus to make out the pixelated words and images on a screen. Over time, the extra effort can strain your eyes.
You blink less – Studies show that people blink three to five times less during screen use. This can dry out your eyes and lead to uncomfortable symptoms. Eye dryness is most common with smartphone use, but it can happen with any other screen too.
Most people use them longer and more often – Every day, four in five American adults use digital screens for two hours or more. The average American office worker looks at a computer screen for around seven hours a day.
Other factors can also contribute to eye fatigue:
Glare – Reflections and other lighting problems can aggravate digital eye strain symptoms.
Position – Studies show that your eyes tend to be more comfortable when they're looking down slightly (about 10 degrees).
Specifications – A screen's resolution (how many pixels it has) and refresh rate (how many times it shows a new image every second) can affect your eyes. For example, the 60-hertz refresh rate of standard computer monitors may create a flickering effect. Choosing a monitor with a higher refresh rate (70 hertz and up) can reduce this effect and help relieve eye strain.
Uncorrected eye problems – Common conditions called refractive errors, along with dry eye and other eye conditions, can worsen eye fatigue if they aren't corrected or treated. Eye doctors can diagnose these problems during a comprehensive eye exam.
How to prevent eye strain
There are things you can do to make your eyes feel more comfortable and relieve eye strain during long stretches of focus. Try to incorporate as many of these methods as possible into your daily routine:
1. Take more breaks
Regular breaks are a simple and effective way to rest overworked eyes and tired muscles.
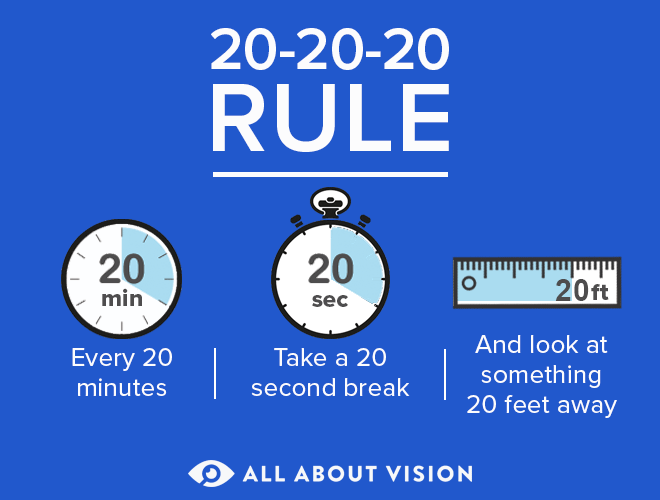
The 20-20-20 rule is one way to reduce eye fatigue. The steps are simple: For every 20 minutes of screen use or other high-focus activity, take a 20-second break to look at something at least 20 feet away.
If it's hard for you to remember to take breaks, try using a kitchen timer or smartphone app to remind you each time 20 minutes pass.
Add a longer, 15-minute break for every two hours of continuous focus.
2. Limit screen time when possible
People are more at risk for digital eye strain when they regularly spend at least two hours in a row looking at screens.
While it can be hard to reduce your device usage for work, you may be able to cut down on personal screen use. Aim for less than four hours of screen time per day, as often as you can.
3. Take "blink breaks"
Most people blink less — and don't fully close their eyelids — when they use a digital device. These habits happen on their own, without consciously thinking about them.
Place a note on your desk or set a phone reminder to take quick "blink breaks" during long stretches of screen use. These extra blinks can help reduce eye dryness and visual discomfort.
Alternatively, take a few moments to sit with your eyes closed. This may also soothe your eyes and may be easier to remember.
4. Avoid direct airflow
Airflow from a fan, air conditioner, heater, or even an open window can evaporate your tears more quickly. During extended focus periods, the extra air can make your eyes feel drier and more fatigued.
If you can't change the source or direction of the airflow, try to move your screen, chair or desk in a way that limits the amount of air blowing into your eyes.
This isn't only important during computer use. For example, the air vents in a car can just as easily dry out your eyes and worsen eye strain while driving. Make sure these vents aren't pointed at your face, especially during long trips.
5. Tweak your surroundings
The environment around you can be just as important as the device or activity itself. Experiment with these strategies to see if they improve your eye strain:
Use a humidifier to add moisture to the air and reduce eye dryness.
Avoid reflections from ceiling lights, lamps, windows and other light sources. Anti-glare screens may help some people feel less eye fatigue.
If you're in a very bright room, consider turning down the lights or closing the shades. Areas with light levels over 1,000 lux (a measure of brightness) could affect your visual comfort and performance during focus. Several phone apps can measure lux for you.
6. Experiment with device settings
Almost all digital screens can be adjusted to make your eyes more comfortable. You'll often find these options in the "Settings" section of your device. When the screen is separate from the device, like it is with a desktop computer, you can change the settings on the computer and monitor itself.
This general guidance could help you feel less eye strain from your computer or other digital device:
Match your screen's brightness to the light level around you. In other words, your screen should be brighter in bright places and darker in dark areas. Many digital devices have "auto brightness" features that automatically adjust to your surroundings.
Increase your font size to make it more readable. Research suggests that it's easier on your eyes when you use a font size of 12 or higher, along with a dark text color on a light background. (This is the opposite of the “dark mode” setting your device may have.)
Set your contrast level between 60% and 70%. This can reduce digital eye strain by making words stand out more against the background.
Use a refresh rate of 70 hertz or higher. (This won't be possible for everyone since the standard rate for many displays is 60 hertz or less.)
Research suggests that screens with higher resolutions (more pixels and clearer images) cause less computer eye strain. You may be able to change your resolution in your computer or device settings. If it's already set to its maximum resolution, it could be worth exploring a new screen or device.
7. Adjust your ergonomics
Minor posture and placement adjustments can help relieve digital eye strain symptoms during computer work:
Place the screen about an arm's length away. A distance between 25 and 35 inches works well for most people.
The top of your monitor should be at or near eye level. If it isn't exact, slightly below eye level is better than slightly above.
The center of your screen should be around 10 degrees below your straight-ahead eye level. Your eyes should look slightly downward while your head faces forward.
Avoid using laptops flat on a table or your lap. Try to elevate the screen so you can read it without bending your neck.
Make reminders to sit or stand upright if you have a habit of slouching.
Relax your shoulders and rest your feet flat on the floor. This encourages better posture and less muscle tension.
Don't forget to take regular breaks by practicing the 20-20-20 rule.
8. Consider over-the-counter eye drops
Your eye doctor may recommend using over-the-counter eye drops called artificial tears if your eyes are still dry. They're designed to resemble your eye's natural tears.
Dry-eye drops are available with or without preservatives. These chemicals keep the drops fresh but may harm your eye's surface if you use them a lot.
Make sure to discuss any new eye drops with your eye doctor before you try them — even if they don't require a prescription.
9. Wear glasses if you usually wear contacts
Studies have shown that contact lens wearers feel more eye strain when they have their contacts in.
Contacts disrupt the delicate tear film that keeps your eyes lubricated, so they can worsen the dryness that comes with eye fatigue. Glasses don't affect your tear film since they don't directly touch your eyes.
Switching to prescription glasses during long periods of focus could help your eyes feel more moisturized and relaxed. Make sure your eyeglass prescription is up to date so you don't risk adding to your eye strain.
10. Try a new kind of glasses
Certain eyeglass lenses and coatings are designed to make reading and screen use more comfortable:
Computer glasses that filter blue-violet light may improve visual comfort by reducing glare during extended periods of screen use.
Glasses with extra magnification alone (like reading glasses) can help with eye fatigue during near work.
Lenses with anti-reflective coating limit the glare reflecting from lights around you.
Multifocal glasses provide multiple focus zones in each lens, so people with presbyopia can see clearly up close and far away. Progressive lenses, bifocals and trifocals are common types of multifocal lenses.
11. Diagnose and correct any eye problems
You may feel more eye strain if you have an uncorrected (or undercorrected) eye condition.
Refractive errors are very common eye problems that make your vision blurry. Even a small amount of blurriness can make your eyes work harder than they need to.
The main refractive errors are:
Nearsightedness (faraway objects look blurry)
Farsightedness (closer objects look blurry)
Astigmatism (both near and far objects may be blurry)
Presbyopia (closer objects get blurrier sometime after age 40)
Refractive errors can usually be corrected with prescription glasses or contact lenses. Your optometrist or ophthalmologist will give you a vision prescription after your eye exam if they find one of these conditions.
Other eye disorders can raise your risk for developing eye strain and other symptoms too — especially if they aren't treated. Your eye doctor will check for signs of these conditions during your appointment.
When to see an eye doctor
Eye strain can be uncomfortable and even painful, but you can limit its impact to your daily life.
Schedule an eye exam if you experience symptoms of eye strain or any other vision changes. Your eye doctor will work with you to relieve your symptoms and treat any eye problems that could be causing your discomfort.
Eye strain: How to prevent tired eyes. EyeSmart. American Academy of Ophthalmology. May 2023.
Eye strain. Cleveland Clinic. July 2023.
Asthenopia. EyeWiki. American Academy of Ophthalmology. June 2024.
Digital eye strain – A comprehensive review. Ophthalmology and Therapy. July 2022.
Computer vision syndrome. American Optometric Association. Accessed November 2024.
Computers, digital devices, and eye strain. EyeSmart. American Academy of Ophthalmology. June 2024.
Computer vision syndrome (digital eye strain). EyeWiki. American Academy of Ophthalmology. May 2023.
Eye discomfort. UCLA Ergonomics. Accessed November 2024.
Computer vision syndrome. Cleveland Clinic. February 2023.
Higher resolution screens may reduce digital eye strain. Review of Optometry. February 2022.
The use of preservatives in dry eye drops. Clinical Ophthalmology. August 2019.
How contact lenses contribute to dry eye. Review of Optometry. May 2023.
Computer vision syndrome in presbyopic digital device workers and progressive lens design. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics. May 2021.
Refractive errors. National Eye Institute. November 2023.
Page published on Wednesday, February 27, 2019
Page updated on Tuesday, November 26, 2024
Medically reviewed on Wednesday, November 13, 2024






