Argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT)
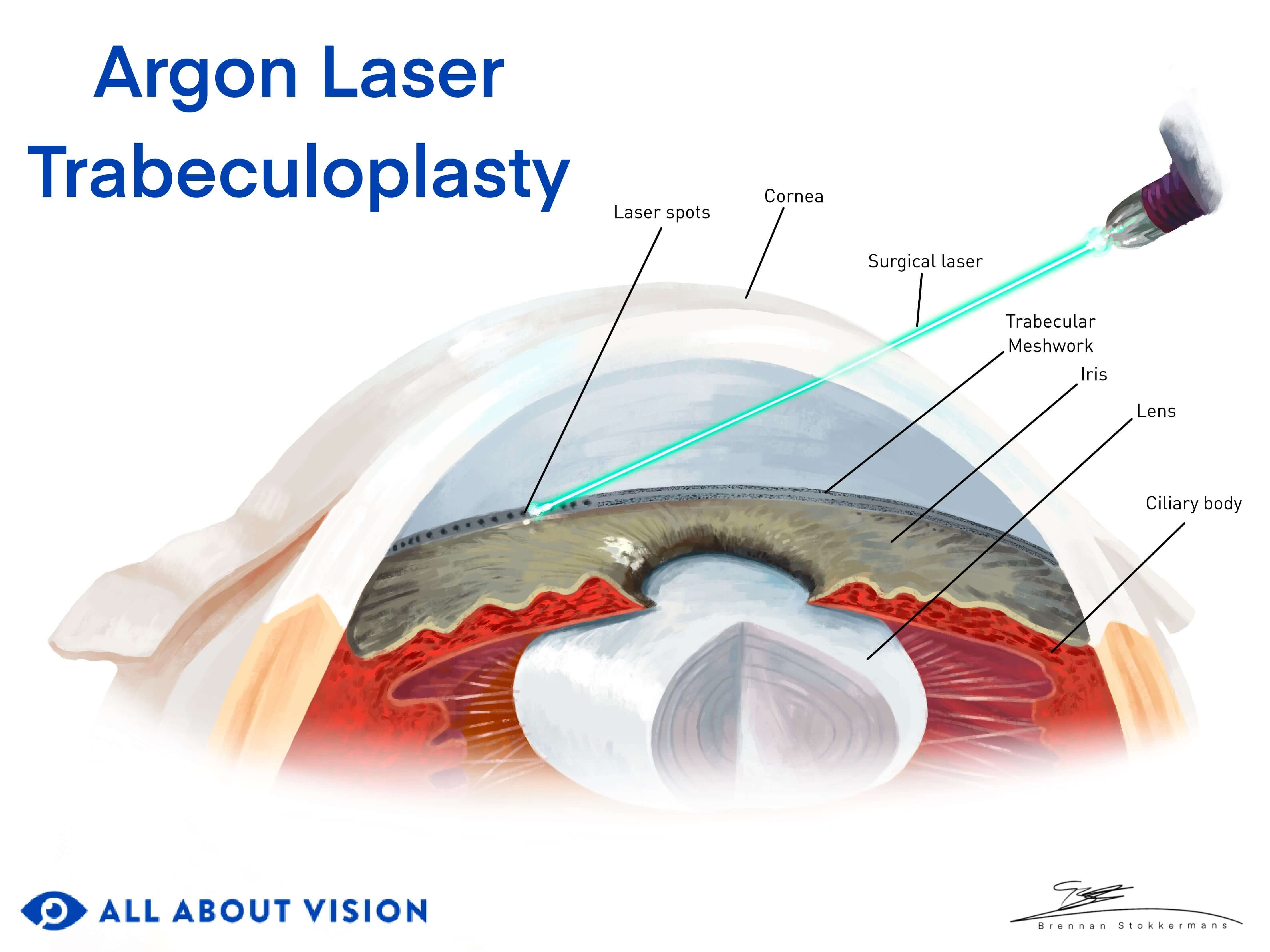
What is argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT)?
Argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT) is an in-office laser procedure used to treat open-angle glaucoma. This type of glaucoma usually occurs due to high eye pressure. The fluid in the front of the eye — the aqueous humor — is not draining properly. ALT helps increase the drainage to lower eye pressure.
This surgery is similar to selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT). Both procedures use a laser to improve aqueous humor outflow through a spongy drainage meshwork in the eye, lowering eye pressure.
ALT uses a higher-energy laser than SLT. The lower-energy laser used during SLT is absorbed by only particular pigmented tissue in the eye. As a result, SLT usually has less scarring and allows for multiple treatments if needed. ALT does not allow for repeated treatments.
Glaucoma surgery can help lower the pressure inside the eye in people with glaucoma. When the pressure in the eye is too high, the risk of vision loss increases due to damage to the optic nerve, which sends signals from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma surgery cannot recover lost vision but can help prevent further vision loss.
READ MORE: Open-angle glaucoma: Causes, symptoms and treatment
What to expect during an ALT
During the procedure, a laser makes small, evenly spread-out burns in the eye's drainage meshwork, which is called the trabecular meshwork. This helps improve the meshwork's function, gradually reducing eye pressure over one to three months.
An eye drop is placed in the eye to prevent increased eye pressure after the procedure.
An anesthetic drop is applied to numb the eye.
A clear gel is applied to the eye to cushion the placement of the goniolens.
The lens is carefully placed on the eye to help focus the laser on the trabecular meshwork. This lens also keeps you from blinking and keeps the eye stable.
A series of laser pulses are targeted at the trabecular meshwork. During this process, clicking sounds and flashes of light may occur.
The doctor may need to rotate the lens slowly as they treat different areas of the trabecular meshwork.
When the procedure is finished, the doctor will remove the lens.
The procedure may cause mild discomfort. On average, the entire process takes five to 10 minutes. After the laser treatment is finished, the gel in the eyes may take up to an hour to clear.
After laser surgery, the pressure in your eyes may initially be normal but increase rapidly within one to four hours. To prevent this, the doctor may give you medication before or after the surgery, especially if you had high eye pressure before the procedure.
Your doctor will monitor your intraocular pressure to ensure it remains within a normal range. You may be prescribed anti-inflammatory eye drops for a few days. You will need to be seen again in one to two weeks, around one month and after several months.
Be prepared to have someone drive you home after the procedure. It is important to avoid any excess strain for the remainder of the day. You can use electronic devices if you wish. If you feel any mild discomfort, ask your doctor if you can take Tylenol.
Contact your doctor if the discomfort becomes unbearable or your vision suddenly declines. The day after the procedure, you can return to your regular routine.
Benefits and risks of ALT
Argon laser trabeculoplasty is an overall safe procedure, and complications are rare.
Benefits
ALT effectively reduces intraocular pressure, which is critical for preventing vision loss. The procedure can be performed without needles and injections in an outpatient setting. Due to this, the day after the procedure, you can return to your normal activities.
Risks and complications
ALT can cause more discomfort and scarring than SLT. Although complications are not common with laser trabeculoplasty, they can include:
Elevated pressure in the eyes – This is the main risk associated with laser surgery for glaucoma. Your eye doctor will put eye drops in before and after the procedure to prevent this.
Temporary inflammation of the iris – The iris is the colored part of the eye. It can become irritated due to the procedure.
Cloudy appearance of the cornea – This is usually temporary and goes away quickly.
Blockage of the angle – The cornea and iris can stick together, blocking the drainage angle.
Discomfort – In most cases, Tylenol can be taken for relief.
Blurry vision – This is usually temporary, and vision will return to normal after a short time.
What is the success rate for ALT?
Approximately three-quarters of people who have not had eye surgery before have a significant drop in eye pressure after argon laser trabeculoplasty.
Researchers have found that ALT and SLT reduce eye pressure about equally. As time passes, ALT can become less effective. It is not uncommon to still need medication after laser surgery in order to keep eye pressure in the normal range.
READ MORE: Glaucoma treatment: Eye drops, oral medications, surgery and more
ALT vs. other laser treatments for glaucoma
A laser can be used to perform several types of in-office glaucoma surgeries, and only numbing drops are usually required. You may need other types of glaucoma surgery if medication and laser surgeries haven’t been effective. These may require an incision, and local anesthetic may be necessary.
ALT vs. SLT: Understanding the differences
ALT uses a higher-energy laser than SLT, which increases the amount of scar tissue, making it unrepeatable. For this reason, SLT may be considered a first line of treatment for people with open-angle glaucoma, while ALT is not. Both in-office procedures take five to 10 minutes and only require numbing drops.
Laser peripheral iridotomy (LPI)
Laser peripheral iridotomy is commonly used to treat narrow-angle glaucoma. It is also a preventive measure against glaucoma attacks in individuals with narrow angles. The angle is the junction at which the iris and cornea meet. A narrowing of the angle can cause a sudden increase in eye pressure because this is where aqueous humor flows out of the eye.
Narrow-angle glaucoma requires different surgery than open-angle glaucoma. In narrow-angle glaucoma, the meshwork drains normally, but the drainage angle has narrowed or closed. The laser in LPI makes a small hole in the iris, increasing the outflow of aqueous humor.
Speak to your doctor
Glaucoma is a vision-threatening eye condition. High intraocular pressure is a major risk factor, and keeping it within a normal range is critical. Contact your doctor if you have additional questions about glaucoma eye surgeries. They can further explain the medical and surgical options that are most appropriate for your condition. In addition, always follow your doctor’s guidance about routine and follow-up appointments. This is important for monitoring the progression of any eye conditions.
READ MORE: Types of eye surgery and the conditions they treat
Laser trabeculoplasty: ALT vs SLT. EyeWiki. American Academy of Ophthalmology. December 2023.
Laser trabeculoplasty. Department of Ophthalmology. UCLA Health. Accessed May 2024.
Glaucoma surgery. University of Virginia Health. Accessed May 2024.
Selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT). Wills Eye Hospital. Accessed May 2024.
Laser trabeculoplasty for glaucoma. MyHealth.Alberta.ca (Government of Alberta). June 2023.
Glaucoma. Penn Medicine. August 2022.
Laser peripheral iridotomy. Wills Eye Hospital. Accessed May 2024.
Page published on Friday, July 12, 2024
Page updated on Tuesday, July 16, 2024






