Why does my doctor want to dilate my eyes?
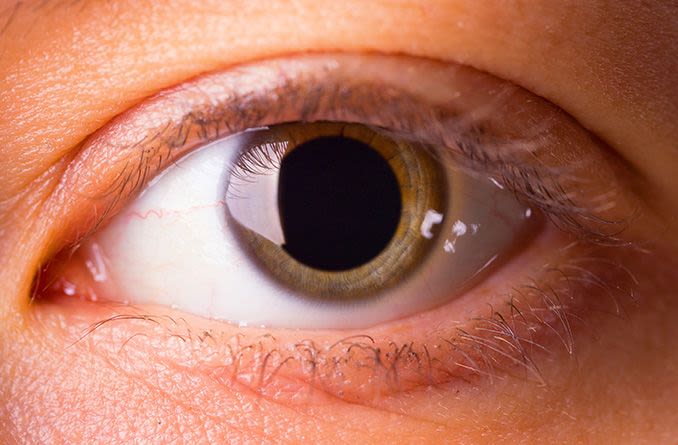
Why do you need your eyes dilated?
Pupil dilation is an important part of your regular eye exam because it allows your doctor to get a better look inside your eyes. After dilating drops cause your pupils to grow in size (dilate), your doctor can more clearly see various parts of your eyes, including the optic nerves, retinas and blood vessels.
This better view can help doctors more quickly and easily diagnose a host of diseases, both eye-related and not, including:
High blood pressure
Diabetes
NEED AN EYE EXAM? Find an eye doctor near you and schedule an appointment.
Is eye dilation necessary?
Whether your eye doctor recommends eye dilation as part of your eye exam depends on a variety of factors, including your age, ethnicity, overall health and risk of developing eye disease.
The National Eye Institute recommends an exam with dilation every one to two years if you:
Are over age 60
Are African American and over age 40
Have a family history of glaucoma
If you have diabetes or high blood pressure, you should probably have a dilated eye exam at least once a year. To find out what’s best for you, talk to your eye doctor.
How long will eye dilation last?
Once your eye doctor administers the drops, your eyes should fully dilate in 15 to 30 minutes. The dilating effects of the drops — including light sensitivity, blurry vision, a slight stinging sensation and difficulty focusing on near objects — last between four and six hours for most adults.
Children often feel the effects for up to a full day, and people with a lighter eye color can experience longer-lasting effects as well.
To protect your light-sensitive eyes following the exam, take sunglasses to your appointment or ask your doctor for disposable shades before you leave.
How long after your eyes are dilated can you drive?
You can drive immediately following eye dilation, but it is recommended that you take someone with you to your first dilation appointment to see how your eyes react before hitting the road.
If you decide to drive yourself, take extra caution and wear your sunglasses, or the ones provided to you, until the dilation wears off.
Can eye dilation cause other problems?
For most people, the most aggravating side effect of eye dilation is light sensitivity.
Some people may also experience a slight sting when the drops are administered, blurry vision and difficulty focusing on near objects. Headaches have also been reported, usually as a result of increased light sensitivity.
These side effects can be more dangerous in elderly patients whose mobility is already affected.
In rare cases, more extreme reactions have occurred, including dizziness, increased blood pressure and allergic reactions.
Is Optomap a substitute for dilation?
New technology, such as Optomap ultra-widefield retinal imaging, allows doctors to view the retina without the need for dilation.
Optomap enables this view via a series of images produced by a laser ophthalmoscope that digitally scans the retina. The scan captures a 200-degree view of the retina — compared with the 45 degrees eye doctors can generally see in a dilated eye — and can be stored for future comparison.
While there are benefits to new retinal imaging technology, the scan may be an added cost to your basic eye exam. There also have been cases in which traditional dilation and ophthalmoscopy detected retinal holes that the imaging failed to capture.
A 2017 study in Seminars in Ophthalmology found that “ultra-widefield imaging failed to detect retinal holes in the superior and inferior quadrants in 11.1% and 19.4% of cases, respectively.”
READ NEXT: What not to do after eye dilation
Page published on Friday, January 10, 2020




